Netting
General features
Elements
Types & dimension
References
S
T
U
V
FN
FT
WN
VN
TO
DE
CO
Colours available in blue / green. Other colours please consult availability before ordering.
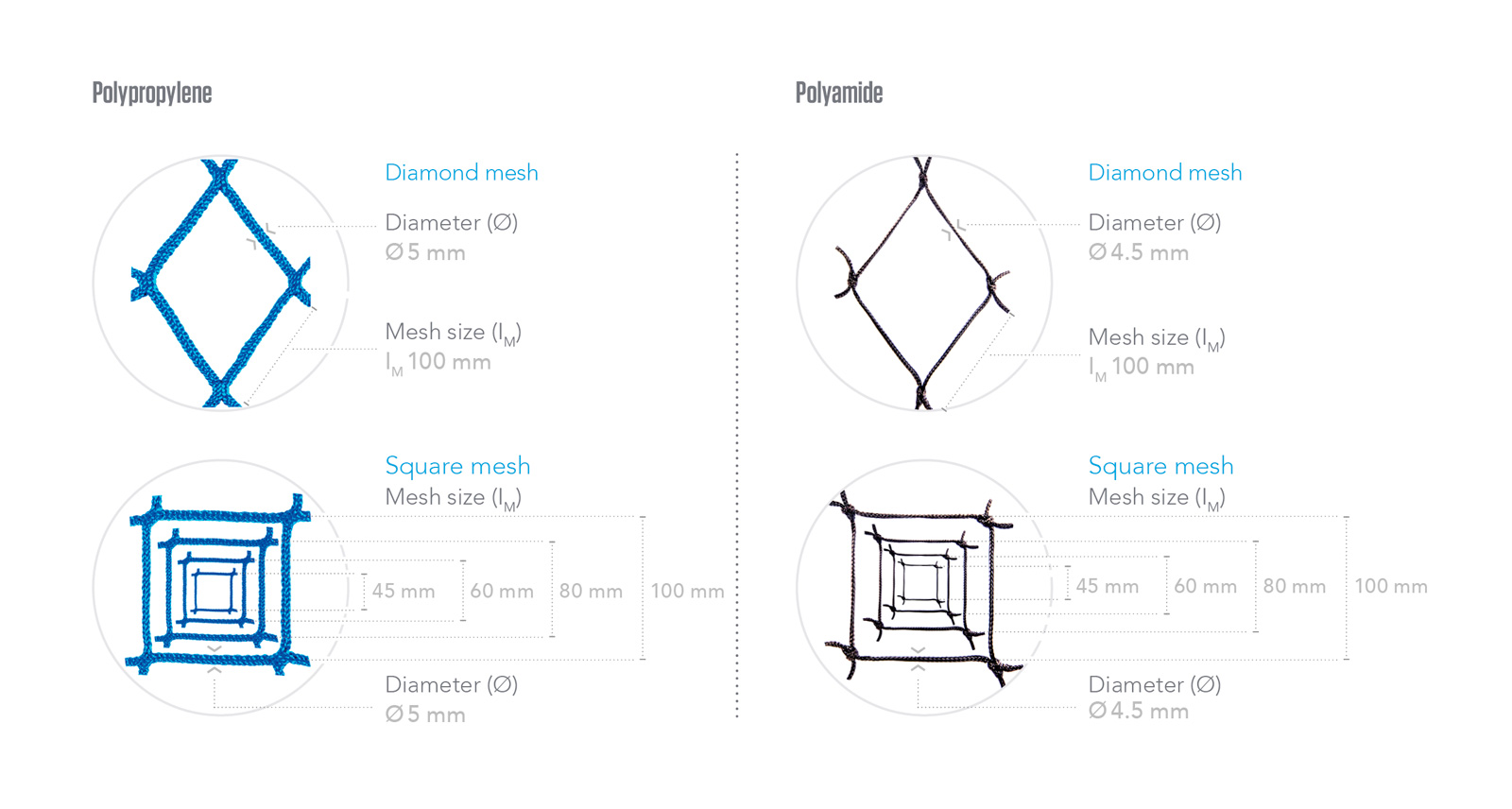
Materials
In Visornets we produce our nets using the best yarns in the market, an strict suppliers control allow us to keep the same quality in our safety netting production at anytime.
Visornets only use for their safety nets production lines polypropylene high tenacity yarn and technical polyamide high tenacity 6 yarn, both treated with the most exigent UV treatment.
Polypropylene high tenacity
Properties of Polypropylene Fibres
Specific Gravity
0.90 – 0.91 gm/cm3
Because of its low specific gravity, polypropylene yields the greatest volume of fibre for a given weight. This high yield means that polypropylene fibre provides good bulk and cover, while being lighter in weight. Polypropylene is 20% lighter than nylon.
Anti-Static Behaviour
Resistant to Bacteria and Micro-organisms
Polypropylene fibres are not attacked by bacteria or micro-organisms
Environmental Effect
Recyclable, ecologically friendly.
Effect of Heat
The melting point of polypropylene is about 165°C and while it does not have a true softening point temperature, the maximum processing temperature of the fibre is approximately 140°C. Prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures will cause degradation of the fibre, but anti-oxidants are incorporated in polypropylene fibres to protect them during processing and at normal service temperatures.
The shrinkage
The shrinkage of polypropylene fibre is controlled by its manufacturing conditions. At textile processing temperatures, which do not normally exceed 130°C., the shrinkage varies between 2.5% to 5%.
Effect of Extreme Cold
Remains flexible at temperatures in the region of -55°C.
Flammability
Polypropylene fibre burns and presents much the same risks as most other man-made textile fibres. It can, however, be rendered flame-retardant by the incorporation of additives.
Colour Properties
Fade-resistant. Polypropylene is dope-dyed (melt-dyed), which is the most “colourfast” of any colouring methods, and produces fibres and yarns that are colourfast, washfast, lightfast and fade-resistant. The colour is incorporated within the fibre itself.
Resistance to Sunlight
Strength, colour fastness and degradation can be effectively protected by means of stabilizers.
Effect on Strength
Ultraviolet (UV) absorbers and stabilizers are incorporated in polypropylene fibres to give them the required degree of UV resistance and stability.
Colour Fastness
The normal method of colouring other fibres is by dyeing. The minimum colour fastness rating required for fibres in many applications is 4 – 5 (BS 1006) and ratings in the range of 4 – 6 are normal. However, polypropylene fibre is coloured during production by pigmentation – often called ‘dope dyeing’ or ‘melt dyeing’. The pigments used for polypropylene fibres give very good light fastness ratings of 7 and 8.
Effect of Acids
Excellent resistance to most acids except chlorosulphonic and concentrated sulfuric acid.
Effect of Alkalis
Excellent resistance with the exception of some oxidizing agents.
Effect of Bleaches and Solvents
Excellent resistance. However, chlorinated hydrocarbons cause swelling at room temperature and dissolve polypropylene at 71 °C. and higher.
Abrasion resistance
The abrasion resistance of polypropylene approaches that of nylon and is superior to that of other fibres, and is good even when wet.
Resistance to Water
- Water Absorption: The water absorption of polypropylene fibre is about 0.3% after 24 hours immersion in water.
- Effects on Strength: Water has no effect on the strength of polypropylene fibres.
- Dimensional Stability: Because polypropylene fibres absorb hardly any moisture their dimensions do not alter with changing humidity or when they become wet.
- Quick Drying: Polypropylene is hydrophobic and will not absorb water in the fibre. Water “wicks” away from the skin and through the fabric to the face for quick evaporation.
Polyamide high tenacity
Polyamide technical properties
Not significantly affected by water
A slight drop in tenacity when immersing in water is fully reversible on drying. The standard regain of nylon is 4.5 % of water.
Melting point
6.6 melts at 250°C and nylon 6 at 225°C.
On burning, nylons burn less readily than cotton and rayon and tend to melt away from the flame.
Nylon fibres have a tendency to be self- extinguishing. However, in bulk, a molten mass will burn fairly readily. On burning, nylon has a characteristic celery-like odour.
Nylon has good general resistance to acids, but will disintegrate on heating with concentrated acids.
Nylon is soluble in boiling 80 % acetic acid and in formic acid at room temperature. Nylon is resistant to alkali.
Nylon is not affected by the standard hydrocarbon, aromatic or chlorinated solvents.
Nylon is soluble in phenols, especially in-cresol.
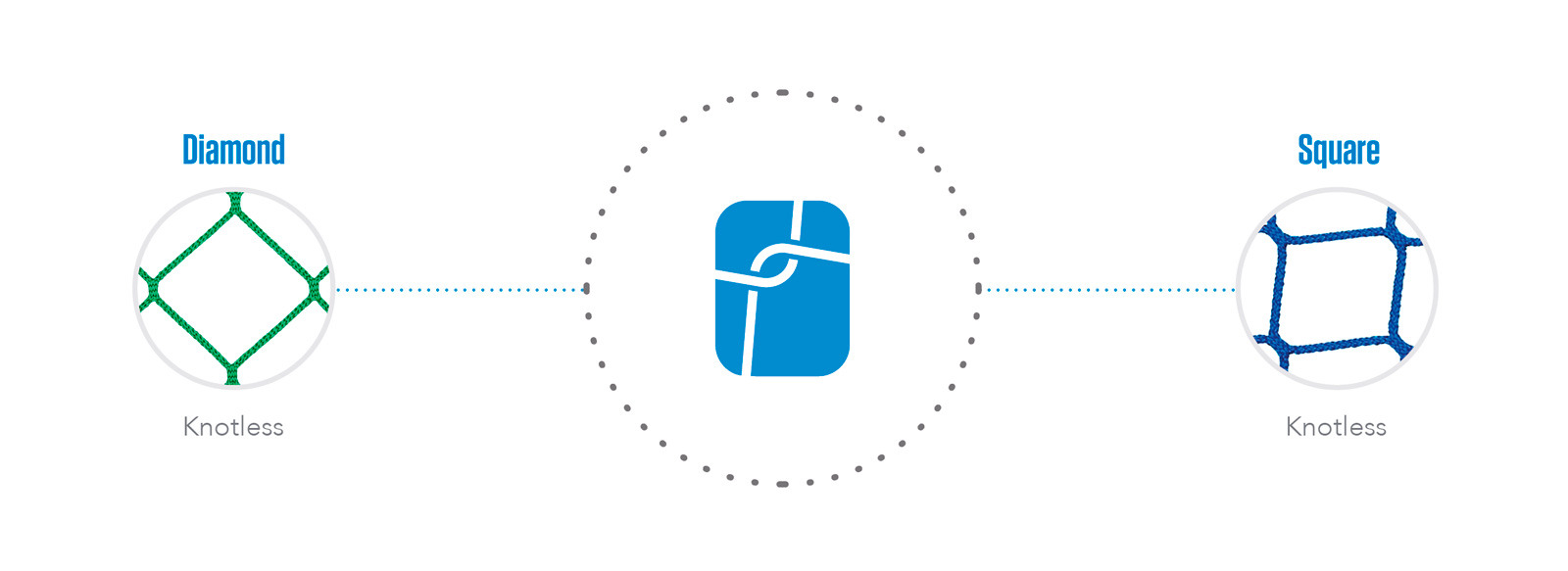
Net finishes
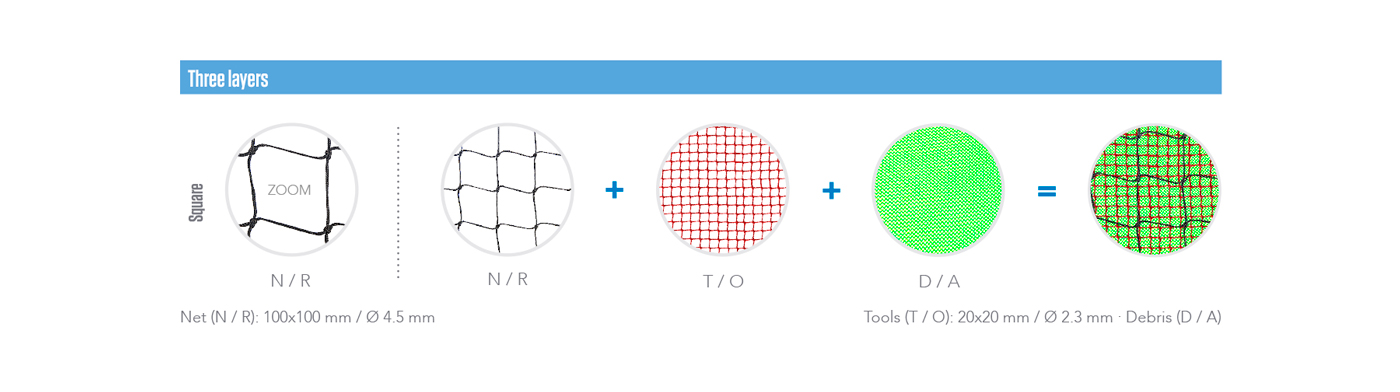
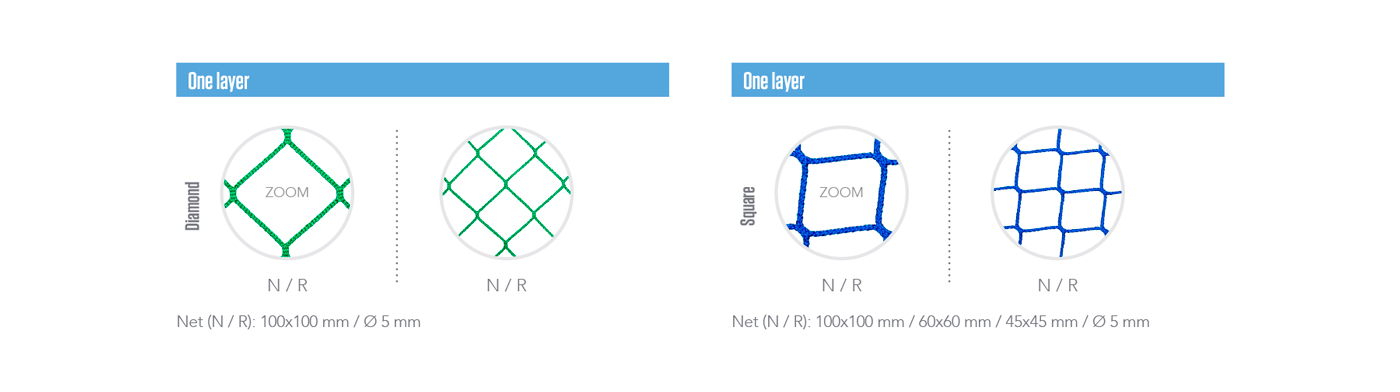
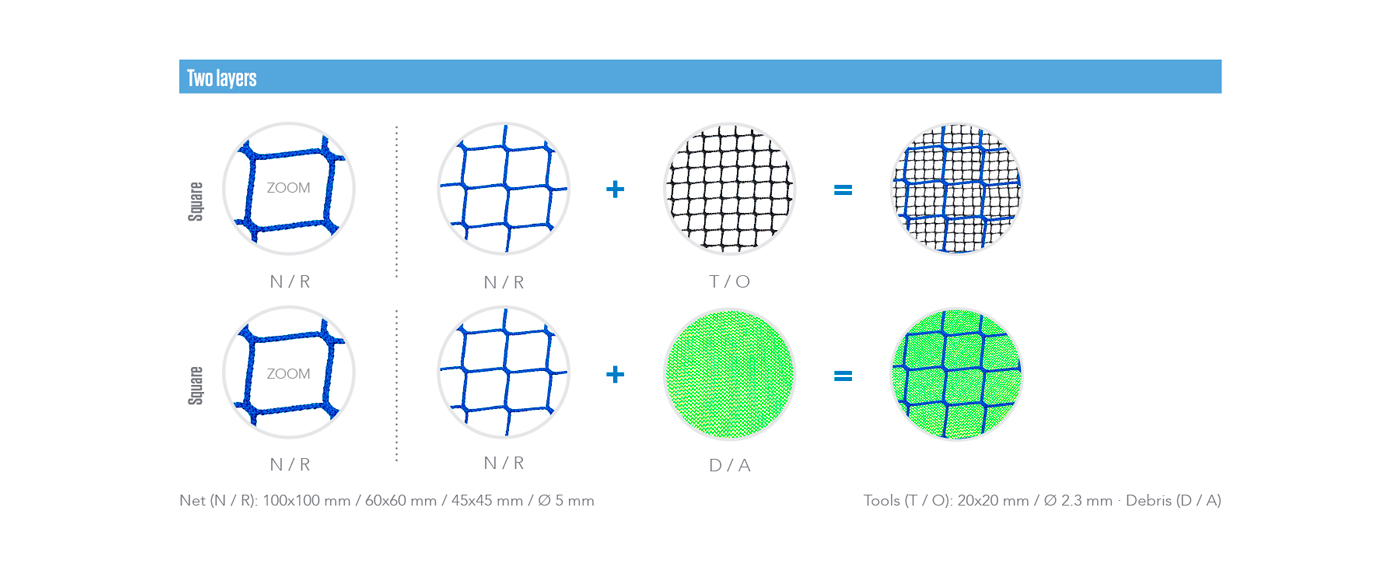
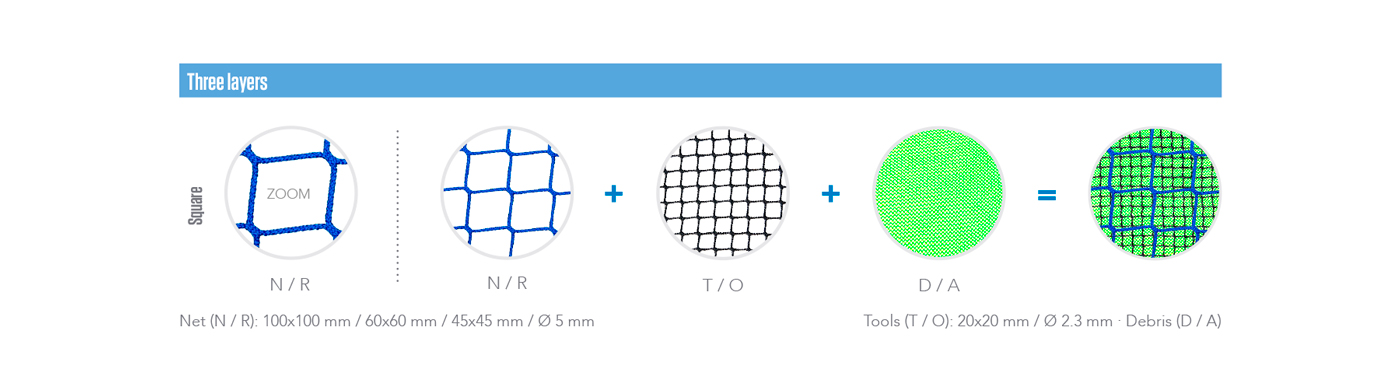
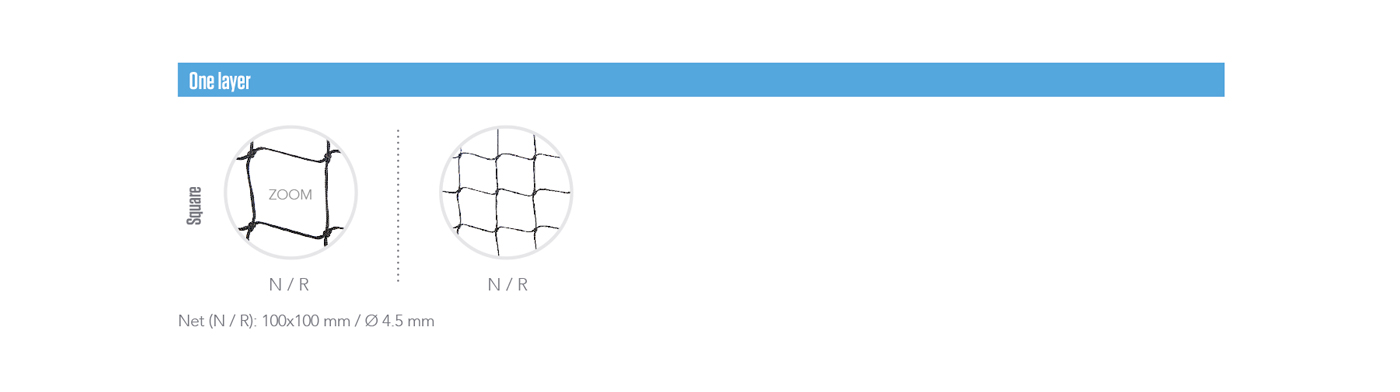
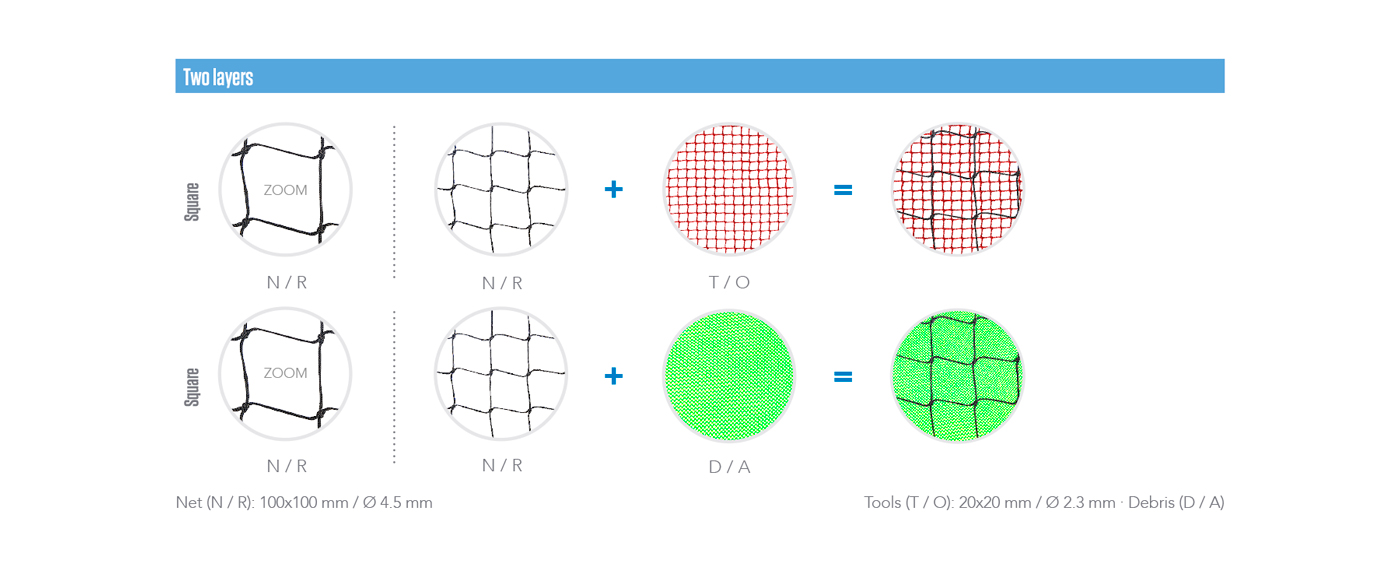
The safety nets can be composed by one, two or three layers. The different types are composed with the combination of three types of meshes: main net, tools and debris.
Layers & types
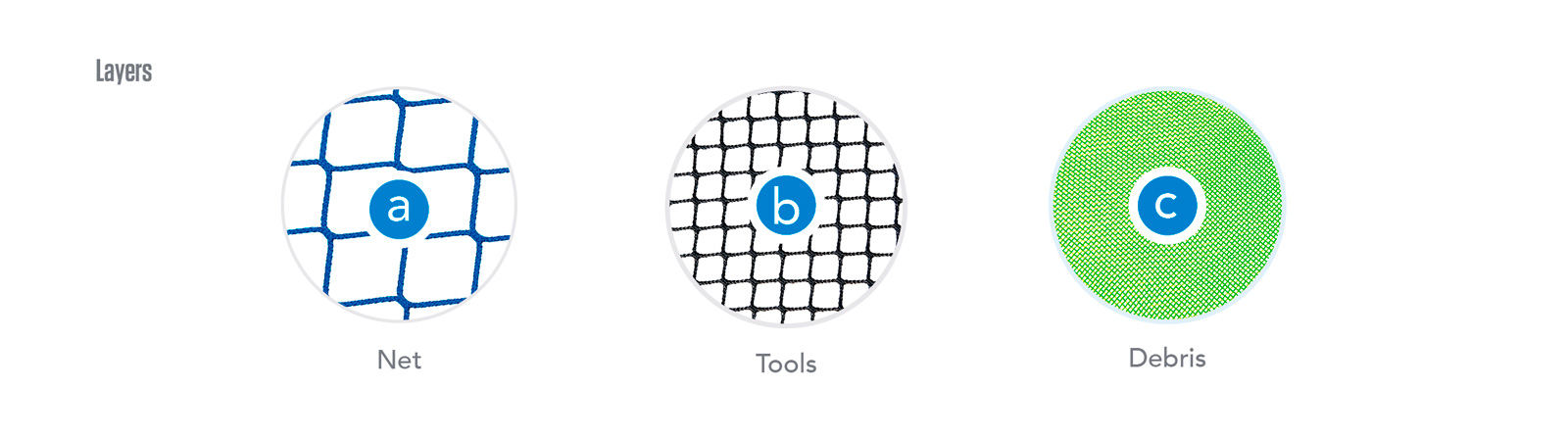




Polypropylene high tenacity net finishes

ONE LAYER

TWO LAYERS

THREE LAYERS

Polyamide high tenacity net finishes

ONE LAYER

TWO LAYERS

THREE LAYERS